EDA Foundations Blog Pages
Tech sprint-1
What are the differences between relative, absolute, and fixed positioning?
Here I hope to break down ‘relative', ‘absolute' and 'fixed positioning'. You may ask yourself “Are we talking about, your great great grandmother relative? No! Absolutely not. Let’s make sure our 'position' is ‘fixed’ and we are ready to break this down in simple terms.
Firstly what do these CSS tags look like in our text editor when we are writing code!?

Breakdown
In basic terms which ever one of these instructions we assign to our chosen HTML element (inside our CSS file) using the property ‘position’ and then the chosen instruction, it will then change the position of that HTML element accordingly to whichever one we chose to use (relative, absolute or fixed).
Why may we need to use these?
If we have an element on our website for example an image (img) then we will need to figure out where we want this to sit on the page and what relationship it has with the other elements on our page around it. We can’t have everything on the page on top of each other (we won’t see what we need to see) or all moving around everywhere when we scroll (We might get motion sick and vomit all over our laptop, cool).
Here we go!
First off know that HTML elements positions are set to ’static’ by default, nothing special they just follow the flow of the page you have made. You can use top, left, bottom and down properties to first get the element to where you want on the page if you wish.
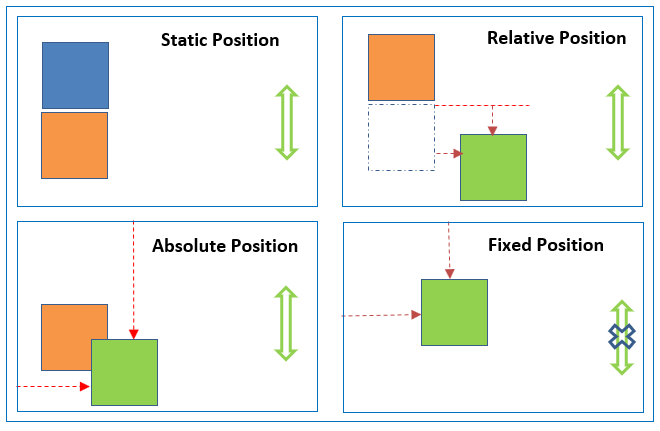
position: relative;
keeps the element relative (in relation or in proportion to) to it’s original position. This may sound a little confusing. It basically means that if you were to set the ‘position’ to ‘relative’ and then wanted to add another CSS property because you wanted to move it towards the top, right, bottom or left then it would move away from the original position in whichever direction you assign it to move. So it’s direction is relative to that original position it was first in before you did anything. Check out this video if that doesn’t make sense, sometimes seeing it happen makes it click!
position: fixed;
is pretty much what you think it is, when assigned it fixes the element exactly where it is. Like virtually using a hammer and nails to secure this element to the exact spot you are happy with so that it won’t move around, even if someone scrolls up or down on the page. *Hint (useful for menu, navigation or footer elements)
position: absolute;
is unfortunately in no way related to vodka! But a cup of tea is recommended whilst reading this article. Position: absolute; is in the position relative to it’s parent element for example an 'img' within a 'div' element. However! if it has no parent element it is positioned relative to the 'body' of the page and moves along when scrolling.
Checklist!
- Design your page layout on paper!
- Make sure you are in the CSS file.
- Specify the HTML element you are wanting to adjust.
- Assign the ‘position’ property first!!!
- Then choose the instruction of which position you want the element to be.
- Check your syntax!
- …and VOILA!!!!! (it worked hopefully) If in doubt take a break and then watch a video on the part you are stuck on. Good Luck!!!